

That’s a super interesting project. For anyone else, the project overview has some great system level diagrams:
https://github.com/opentraffic/otv2-platform
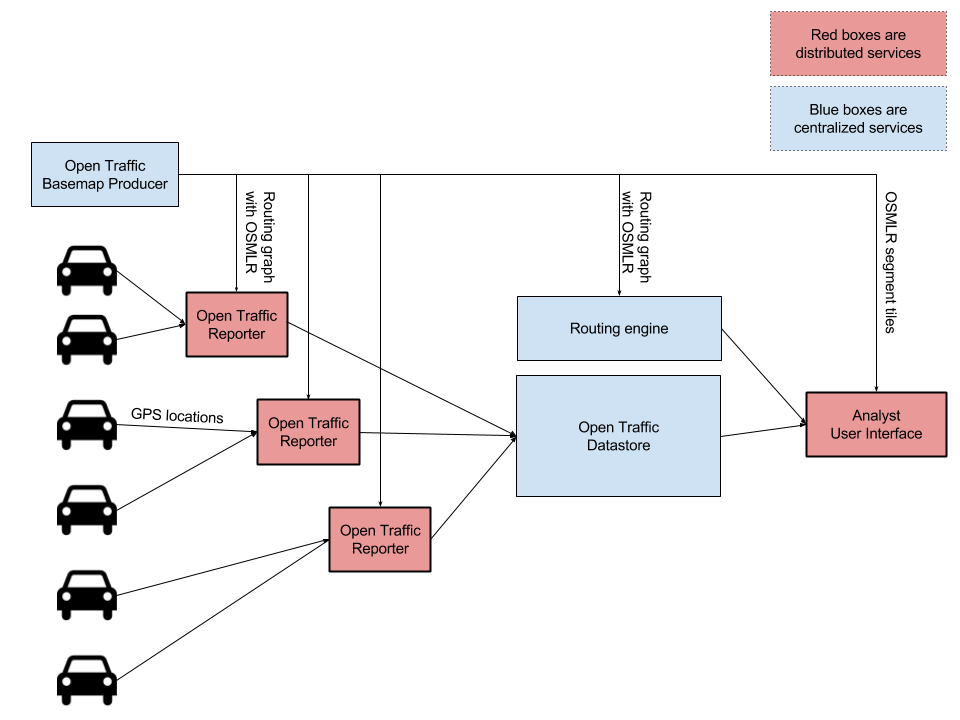


That’s a super interesting project. For anyone else, the project overview has some great system level diagrams:
https://github.com/opentraffic/otv2-platform



time for some kind of anonymizing location data sharing service, peer to peer or federated protocol? that might be interesting, or sketchy, not sure which.


Pretty sure you can download the maps ahead of time, GPS doesn’t require data, then upload the fixes when you get home.


Go map keeps crashing for me, does it for you?


I’ve been using Go Map! but it keeps crashing… Maybe I’ll try Streetcomplete if it’s on apple.


Crawling and indexing lemmy inter-instance would be an incredible boon to discoverability on the platform.
Do it! it is easy to do at home! Just wear some gloves and safety glasses, those jars can easily shatter during the heating process if you use too hot of a heat source. I recommend a glass top electric stove, or put some kind of metal plate between your jar and the burner to help spread out the heat. Once you seal the jar, take it off the heat right away, so it doesn’t build pressure. I boiled mine for a few minutes before sealing to try and get some of the devolved gasses out, and lightly set the lid on top to help the steam push out all the air.


It does. And Firefox is my default browser app.
Yes definitely. The pressure will drop along the vapor pressure curve all the way to the triple point, gently boiling all the way if you remove the heat from the vapor and not directly from the water.
Anything for posterity
Exactly. it was bottled at atmospheric pressure while it was boiling, so 1 atm and 100 degrees C. Check this graph to see the relationship between the water’s temperature and it’s pressure in the jar (since there is no air, only water vapor). If the vapor is condensed, then the pressure drops below the curve on the graph, that is, the pressure in the jar is lowered below the vapor pressure of the water. Any time the pressure is below the vapor pressure, the water will boil, releasing vapor, until the pressure is equal to the vapor pressure. The pressure does not become negative, it is still positive, just lower than the vapor pressure at the given temperature. You can get below the vapor pressure curve by changing the temperature too, which is what we usually do when boiling water at a pressure near 1 atm (760mmHg)
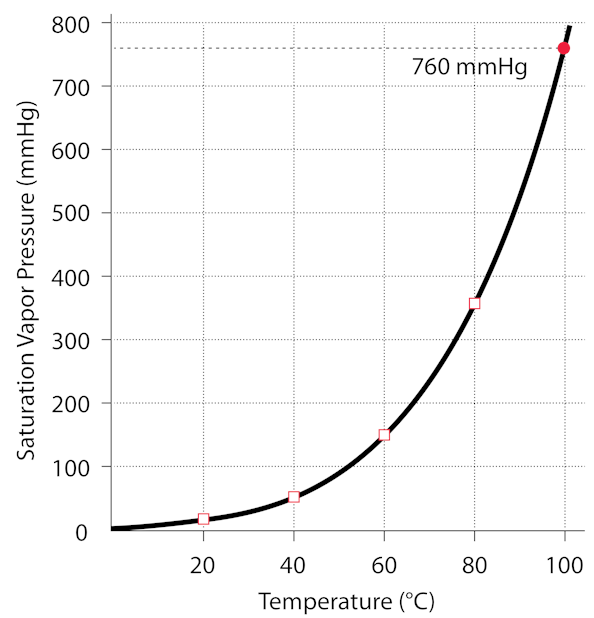
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Kinetic/watvap.html#c2
(1 atmosphere is ~760mmHg)
a slight aside, there is an important difference between the total pressure of the air, and the partial pressure of water vapor in the air. Inside the jar, the two are equal, but in a dry location (not humid) the partial pressure of water vapor is usually less than the vapor pressure of water at that temperature, but since the total large pressure of the atmosphere would not allow a pocket/bubble of very low pressure water vapor to form inside the bulk water, the water cannot boil, but it will evaporate at the surface anyway until the partial pressure of water is equal to the vapor pressure (very humid).
I decided to translate the worksheet into GLSL code on shadertoy. It was really cool to see the gradients and sub-coordinate systems represented by the intermediate variables in the calculation. Smoke and mirrors. Maybe you might have some insight into some of the calculations. https://www.shadertoy.com/view/cllBzM
Any ideas?
I was thinking of doing three separate GOL simulations, one on each RGB channel, and letting the colors mix that way into like 6 colors. right now, I clamp the pixel brightness values to 0 or 1, so that’s why it’s black/white, or rather black/green.


2nd on the keep notes suggestion. I work on lots of unrelated projects, and each time I end up learning a bunch of new command line utilities, so I try to leave behind a text file describing some of the most useful commands I’d discovered that day. Usually helps me come back to a project and not be back at square one every time.


I thought there was something slightly peculiar about the narration.


I hear you, but genetic change at the level of these diseases and traits can take on the order of hundreds of thousands of years or more to accumulate into meaningful trends. Social society is a part of that process, in the way it might be for other social animals. If social dynamics tend to result in communities harboring vulnerable individuals, then there is probably some selective advantage to that behavior, not the other way around.


This is a common misconception. These traits are not likely due to modern medicine (which is very, very new compared to the scale of human evolution). The environment plays a big role, but there is always a distribution of traits in a normal population, some good, some bad. Not to mention that what we might be self-selecting for must change very rapidly as civilizations rise and fall, preferences shift like the winds, and ethics rapidly evolve. I think this misconception can be dangerous, because of what you mentioned. Eugenics.


It’s very difficult and dangerous to be near an MRI ‘shutting down’. Assuming what you mean is turning of the magnet. The magnet is always on, its a coil of superconducting wire submerged in liquid helium with a very large permanent current flowing around it. In order to turn off the magnet quickly, the electric current must be quenched, which can happen if the coil every stops being a super conductor. The current starts heating the coil, causing the liquid helium to boil off, which doesn’t cool the coils as efficiently, and causes a rapid run-away effect where huge volumes of helium explode out of the machine, displacing all the breathable air in the room and blasting all the doors off their hinges, maybe even breaking windows. There’s a lot of energy stored in the coil. It’s not easy to turn it off.
Look up videos of MRI quenching
from that article: “Gallows Humor is, by definition, from the perspective of the victim or at least expressing empathy. If anyone else laughs at the victim or the author tries to make the situation funny, it’s some other form of Black Comedy. This trope is generally when the joke itself or simple laughter allows you to deal with your problems.”
I guess it depends on your perspective. Who’s the victim here.